Abstract
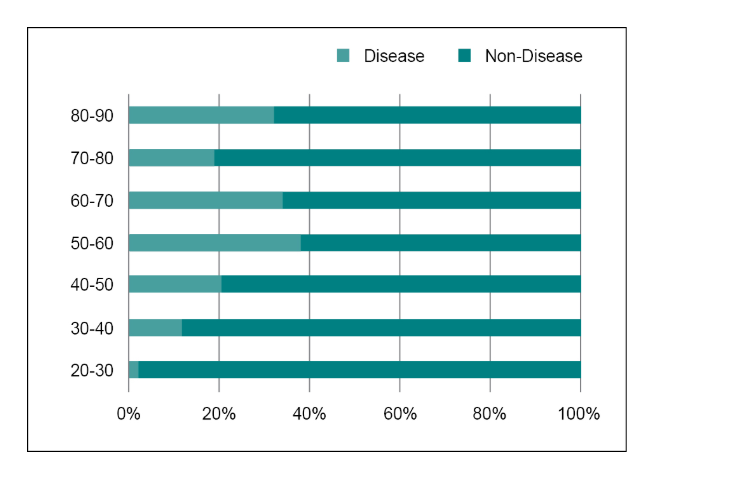
Background: Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) have now become the leading cause of mortality in India. However, there is a gap in prevalence data or national representative surveillance data. Aim: The aim of this cross-sectional study was to evaluate the prevalence of CVD in the urban population of Delhi and the usability of a handheld smartphone-based ECG device “SanketLife” in detecting heart ailments. Material and methods: The study was conducted among 1,521 participants visiting the Perfect Health Mela conducted by Heart Care Foundation of India (HCFI) from 23rd to 27th October, 2018. Known cases of myocardial infarction, hypertension and diabetes were also seen during the study. Results: Of the 1,521 persons screened, 324 (21.3%) were found to have 15 types of abnormalities on ECG after review by an ECG analyst. Tachycardia was detected in 105 (32.4%) persons. Other common findings were intraventricular conduction delay (17.9%; n = 58), premature ventricular contraction (12.6%; n = 41), premature atrial contraction (7.72%; n = 25) and left bundle branch block (6.17%; n = 20). The results also showed a high prevalence of coronary artery blockage (indicative of atherosclerotic CVD) among the study population.Conclusion: The results showed the high prevalence of CVD, particularly in the younger age group and also demonstrated the usability of the device as a point of care test in detecting heart disease in the general population. The effectiveness of such a handheld device can aid in further prevention of avoidable cardiac events and help in better monitoring of CVD.
Download Full PDF
